In the digital age, privacy has become one of the most valuable yet vulnerable assets. Every click, search, and interaction online leaves a digital footprint, which companies, advertisers, and sometimes malicious actors can track. While internet tracking is often framed as harmless or even useful—enhancing user experience through personalized recommendations—the reality is far more complex. Tracking can lead to unwanted profiling, targeted ads, data breaches, and even manipulation of online behavior.
Fortunately, protecting your online privacy is no longer an unattainable goal. With the right strategies, tools, and understanding of digital tracking mechanisms, you can browse the web without being constantly monitored. This article explores how online tracking works and provides a comprehensive guide to browsing the internet with maximum privacy.
Understanding Online Tracking
Before diving into protective measures, it’s crucial to understand how tracking occurs. Online tracking encompasses any method that collects information about your browsing behavior, device, or location. Common tracking techniques include:
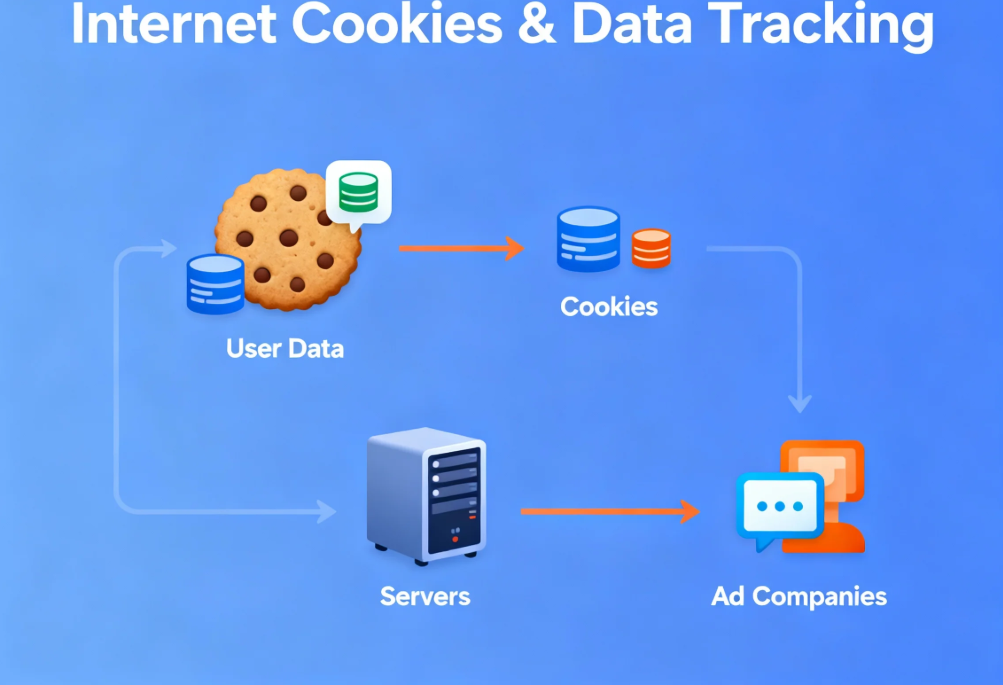
Cookies
Cookies are small text files stored on your device by websites. They remember your preferences, login sessions, and sometimes track your browsing habits across multiple sites. While some cookies are necessary for website functionality (like remembering your cart on an e-commerce site), third-party cookies are often used by advertisers to build detailed profiles of your behavior.
Browser Fingerprinting
Unlike cookies, browser fingerprinting collects information about your device configuration, installed fonts, screen resolution, and browser settings to create a unique “fingerprint.” Even if you delete cookies or use private browsing modes, fingerprinting can still identify and track you across sites.
IP Tracking
Your IP address reveals your approximate location and can be used to track your online activity. While your ISP typically assigns your IP, websites and advertisers use it to deliver location-based content or target you with ads.
Tracking Pixels
Tracking pixels are invisible images embedded in emails or web pages. When loaded, they send information back to the source about when and where the page or email was accessed. Marketers and advertisers frequently use them for monitoring engagement.
5. Supercookies and Evercookies
Supercookies and evercookies are advanced tracking tools designed to persist even after you delete standard cookies. They can store information in multiple locations on your device, making them extremely difficult to remove.

Why You Should Care About Being Tracked
Many people assume tracking is harmless, but in reality, the implications can be serious:
- Personalized Ad Overload: Tracking allows advertisers to profile you and bombard you with targeted ads based on your browsing history.
- Data Privacy Risks: The data collected by trackers can be shared or sold without your consent, sometimes ending up in the hands of malicious entities.
- Behavioral Manipulation: Algorithms can exploit your tracked behavior to influence purchasing decisions, political opinions, and online habits.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Extensive tracking increases the risk of data breaches, as your personal data may be stored across multiple third-party platforms.
Understanding these risks is the first step toward protecting your privacy online.
Steps to Browse the Web Without Being Tracked
Protecting your online activity requires a combination of tools, browser settings, and mindful behavior. Below is a detailed, actionable guide to achieving a high level of privacy.
Use a Privacy-Focused Browser
Traditional browsers like Chrome and Safari are convenient but often collect user data for advertising purposes. Privacy-focused browsers are designed to minimize tracking:
- Mozilla Firefox: Offers enhanced tracking protection, ad blocking, and frequent privacy updates.
- Brave Browser: Blocks ads and trackers by default, integrates with Tor for anonymous browsing, and includes fingerprinting protection.
- Tor Browser: Routes your internet traffic through the Tor network, making it nearly impossible to trace your online activity back to your IP address. Tor is ideal for users who prioritize anonymity over speed.
Tip: Regularly update your browser to ensure you have the latest security patches.
Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A VPN encrypts your internet traffic and masks your IP address, preventing your ISP, websites, and advertisers from tracking your location or online activity. Benefits of using a VPN include:
- Hiding your IP address from websites.
- Encrypting your data on public Wi-Fi networks.
- Accessing geo-restricted content securely.
Choosing the Right VPN: Look for a no-log VPN service that does not store any information about your online activity. Reputable VPNs include ExpressVPN, NordVPN, and ProtonVPN. Avoid free VPNs, as they often monetize user data.
Enable Private or Incognito Mode
Most browsers offer private browsing modes (Incognito in Chrome, Private in Firefox). While this mode:
- Prevents the browser from storing your history and cookies.
- Stops autofill of passwords and form data.
It’s important to note that private mode does not prevent your ISP, VPN, or websites from tracking you. It only limits local storage of browsing data on your device.
Block Third-Party Trackers
Blocking third-party trackers is essential to prevent cross-site tracking. Tools to consider:
- uBlock Origin: A lightweight, open-source ad and tracker blocker.
- Privacy Badger: Developed by the Electronic Frontier Foundation, it automatically blocks trackers that violate your privacy.
- DuckDuckGo Privacy Essentials: Provides tracker blocking, private search, and encryption enforcement.
Pro Tip: Avoid disabling all ads indiscriminately, as some sites rely on revenue from ethical ads. Focus on third-party trackers that compromise privacy.
Manage Cookies Effectively
Cookies are unavoidable in some cases, but managing them minimizes tracking:
- Delete cookies regularly or set your browser to auto-delete cookies after each session.
- Use cookie management extensions to control which cookies are stored.
- Disable third-party cookies entirely in your browser settings.
Tip: Some sites may not function properly without cookies. In such cases, allow cookies only for essential sites while blocking all others.
Use Encrypted Search Engines
Major search engines like Google track every search query and store user data. Consider alternatives that prioritize privacy:
- DuckDuckGo: Does not track search queries or create user profiles.
- Startpage: Uses Google’s search results but removes all tracking.
- Qwant: A European search engine that respects privacy regulations.
Pro Tip: Set your default search engine to a privacy-focused option to prevent accidental exposure of your search activity.
Disable Browser Fingerprinting
Fingerprinting is subtle but pervasive. Steps to mitigate it:
- Use browser extensions like CanvasBlocker or Trace.
- Avoid installing too many browser extensions that could reveal your device fingerprint.
- Enable “Do Not Track” in your browser settings. While not all sites honor it, it’s a worthwhile addition.
Advanced Tip: Using the Tor Browser provides the highest resistance to fingerprinting because it standardizes browser behavior across all users.
Secure Your Online Accounts
Even if your browsing is private, your accounts can reveal personal information:
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for all accounts.
- Use strong, unique passwords stored in a reputable password manager like Bitwarden or 1Password.
- Regularly review account activity for suspicious logins.
Limit Social Media Exposure
Social media platforms are notorious trackers:
- Avoid logging into websites using social media credentials.
- Limit app permissions on your devices, especially location tracking.
- Adjust privacy settings to minimize data sharing with advertisers.
Pro Tip: Consider deactivating or reducing social media usage if privacy is a priority. Many platforms track you even when you’re logged out.
Encrypt Your Communication
Even private browsing is not enough if your communications are insecure:
- Use encrypted messaging apps like Signal or WhatsApp for personal conversations.
- Consider email services like ProtonMail or Tutanota that offer end-to-end encryption.
- Avoid sending sensitive information over unencrypted channels.
Regularly Audit Your Digital Footprint
Your privacy isn’t a one-time setup—it requires ongoing vigilance:
- Search for your name online to see what information is publicly available.
- Remove or update outdated accounts through tools like JustDelete.me.
- Adjust privacy settings on services and devices periodically.
Be Wary of Public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi networks are convenient but insecure:
- Always use a VPN on public networks.
- Avoid accessing sensitive accounts over public Wi-Fi.
- Consider using a mobile hotspot instead of untrusted public networks.
Educate Yourself About Privacy Policies
Many users unknowingly consent to tracking by accepting terms and privacy policies. While lengthy, understanding these policies helps you make informed decisions about:
- Which services collect your data.
- How your data is shared or sold.
- Options to opt out of tracking and targeted advertising.
Balancing Privacy and Convenience
It’s important to acknowledge that achieving complete anonymity online is challenging. Many privacy tools can impact user experience, website functionality, and speed. The key is to find a balance that meets your needs:
- Use VPNs and privacy browsers for sensitive tasks.
- Keep cookies and certain scripts enabled on trusted websites for convenience.
- Layer multiple privacy tools for maximum protection without compromising usability.
The Future of Online Privacy
As digital tracking becomes increasingly sophisticated, user awareness and technological solutions will continue to evolve. Governments, organizations, and companies are slowly responding with stronger privacy regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act). Meanwhile, privacy-focused tools and communities are gaining popularity, providing individuals with the means to reclaim control over their online data.
Being proactive about privacy today not only protects you from tracking but also contributes to a broader cultural shift toward ethical data practices online.

Browsing the web without being tracked is no longer a dream but a practical possibility with the right tools and habits. By understanding tracking methods, employing privacy-focused browsers and VPNs, managing cookies and trackers, securing accounts, and using encrypted communication, you can significantly reduce your digital footprint. While no solution guarantees absolute anonymity, combining multiple strategies empowers you to maintain privacy, minimize unwanted profiling, and browse the internet with confidence.
Your digital life is valuable. Protecting it is not just a technical necessity but a personal right. Implementing the strategies outlined in this article allows you to navigate the web with freedom, security, and peace of mind.