In today’s digital world, nearly every aspect of our lives—personal conversations, financial details, even health records—flows through the internet. While this convenience is transformative, it also exposes us to risks if that information falls into the wrong hands. End-to-end encryption (E2EE) has emerged as one of the most reliable methods for protecting digital privacy. If you’re new to the subject, this encryption guide will walk you through the essentials, helping you build a clear foundation without overwhelming jargon.
What Is End-to-End Encryption?
At its core, encryption is the process of transforming readable data (plaintext) into an unreadable format (ciphertext) using mathematical algorithms. Only those with the correct cryptographic key can convert it back.
End-to-end encryption means that your message or data is encrypted on your device and can only be decrypted by the intended recipient. Even the service provider that carries your message—whether it’s a messaging app, email platform, or cloud service—cannot access the content.
This is fundamentally different from “encryption in transit” (used by many services), where the data is protected as it moves between you and the provider but may be decrypted and re-encrypted once it reaches their servers. E2EE closes that gap, ensuring true confidentiality.
Why Does End-to-End Encryption Matter?
- Privacy Assurance
Without E2EE, third parties—including companies, hackers, or even governments—could potentially read or misuse your data. - Trust in Communication
E2EE enables candid, safe conversations, whether with friends, colleagues, or healthcare professionals. - Resilience Against Breaches
Even if a provider suffers a security breach, encrypted data remains unreadable without the private keys. - Global Standard for Security
From Europe’s GDPR to California’s CCPA, regulatory frameworks increasingly emphasize strong data protection. End-to-end encryption aligns with these expectations.
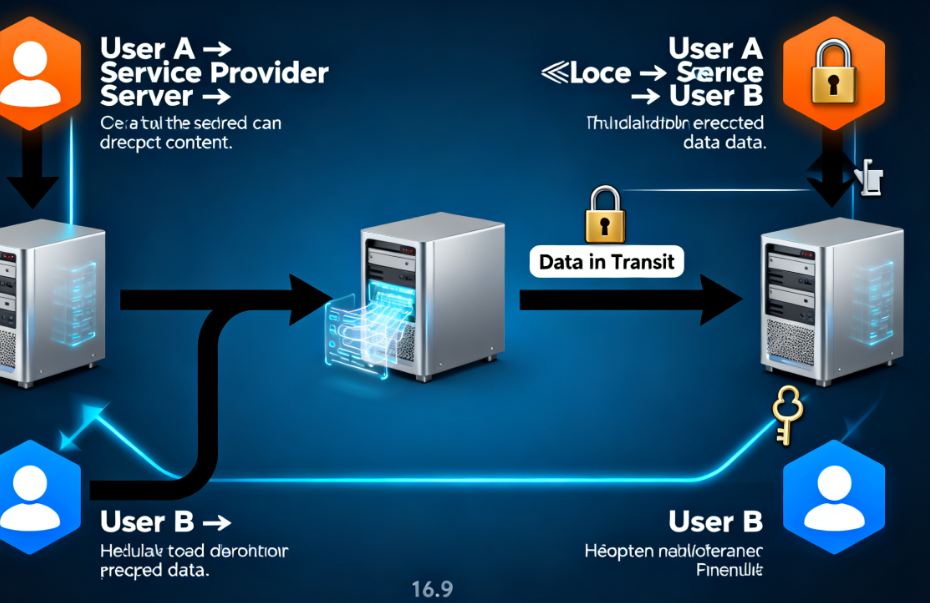
How Does It Work in Practice?
Imagine mailing a physical letter. If you use standard mail, postal workers could technically open and read it. With E2EE, it’s as though you’ve locked the letter in a box that only your recipient has the key for. Even if someone intercepts the box along the way, they can’t open it.
Technically speaking, E2EE relies on:
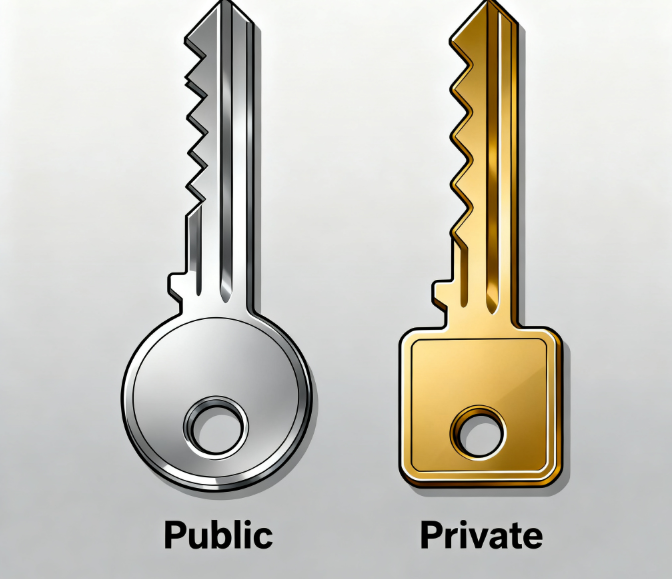
- Public and private keys: A recipient’s public key encrypts the message; their private key decrypts it.
- Session keys: Temporary keys for individual conversations, adding efficiency and forward secrecy.
- Mathematical algorithms: Established standards such as RSA, Diffie-Hellman, or elliptic-curve cryptography.

Where You’ll Encounter End-to-End Encryption
- Messaging Apps: WhatsApp, Signal, and iMessage use E2EE by default.
- Email Providers: Services like ProtonMail and Tutanota offer encrypted email.
- File Storage & Sharing: Some cloud services now include end-to-end encrypted folders.
- Video Calls: Certain platforms extend E2EE to protect meetings and conferences.
Practical Steps for Beginners
If you’re starting out and want to put this encryption guide into practice:
- Choose Tools That Offer E2EE by Default
Download messaging apps like Signal or WhatsApp, or consider encrypted email providers. - Verify Keys Where Possible
Many apps allow you to compare “safety numbers” or QR codes with your contacts to ensure authenticity. - Stay Updated
Keep your apps and devices patched; encryption is strongest when combined with good digital hygiene. - Be Aware of Trade-offs
While E2EE strengthens privacy, it can make features like searchable chat histories or server-based backups less convenient.
Looking Ahead
As global reliance on digital communication grows, so will debates about the balance between privacy and law enforcement access. For individuals, however, learning the fundamentals of encryption isn’t about politics—it’s about empowerment. With a basic understanding of end-to-end encryption, you can make informed decisions that protect your personal and professional data in an uncertain digital landscape.
Final Thought:
Encryption is no longer the exclusive domain of cybersecurity experts or government agencies. By engaging with these concepts now, you’re taking an important step toward safeguarding your digital autonomy.